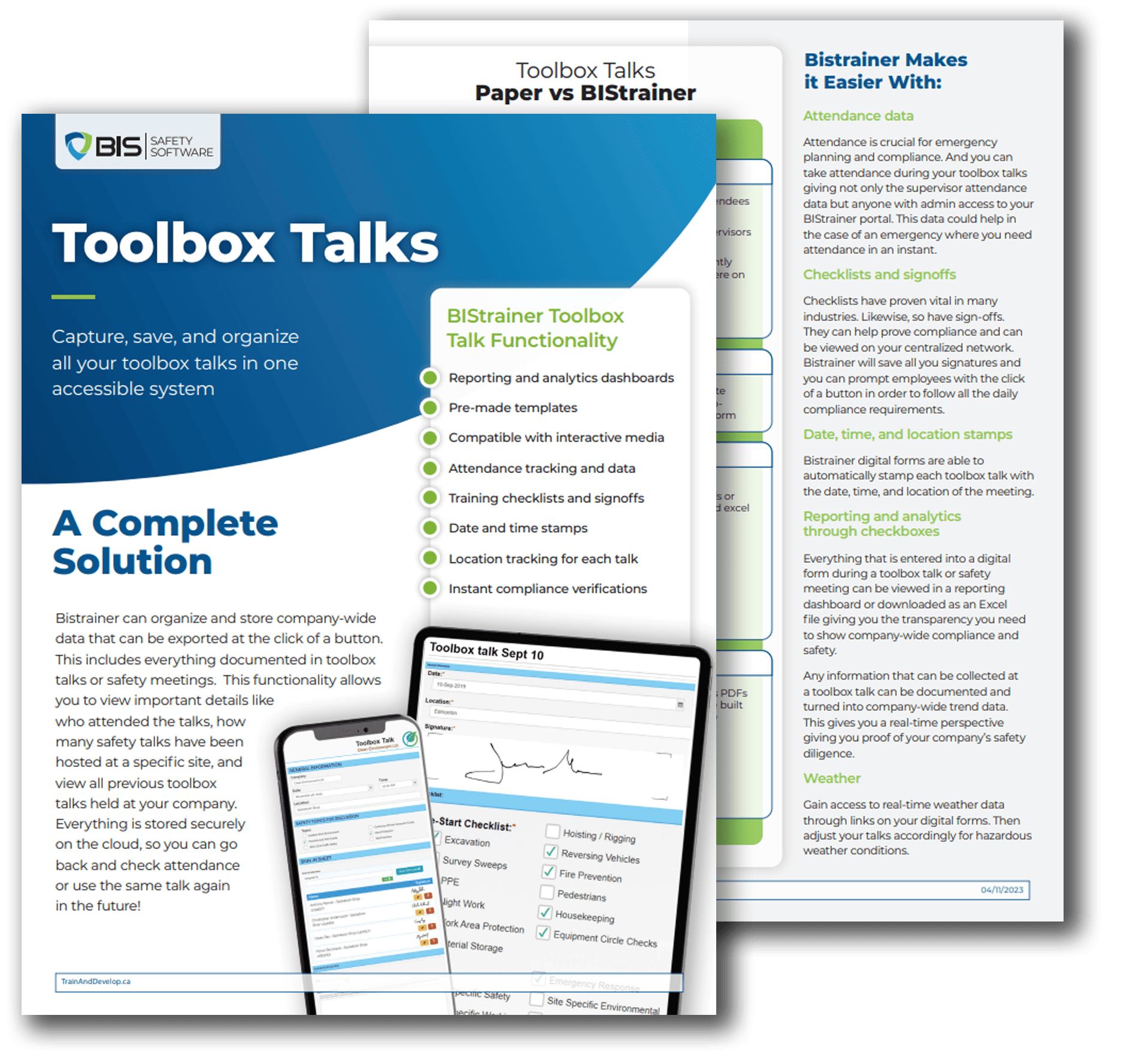
In today’s fast-paced world, safety in the workplace is a top priority for organizations of all sizes. To enhance safety practices, many companies are turning to Safety Management Systems (SMS) and associated tools like Learning Management Systems (LMS), Training Management Systems (TMS), and safety software. These systems offer several key benefits that help keep workers safe and organizations compliant with regulations.
Improved Incident Prevention:
Safety Management Systems (SMS) play a crucial role in preventing workplace incidents, accidents, and injuries. Here’s a more detailed look at how they achieve this:
a. Proactive Hazard Identification: SMS provides a structured framework for identifying and assessing potential hazards within the workplace. This involves conducting comprehensive risk assessments, safety audits, and inspections. By proactively identifying hazards, organizations can take corrective actions before these hazards lead to accidents or injuries.
b. Risk Mitigation: Once hazards are identified, SMS helps organizations develop and implement risk mitigation strategies. This includes defining safety procedures, providing safety training, and ensuring the availability of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). By addressing risks head-on, SMS reduces the likelihood of incidents occurring.
c. Data-Driven Insights: Safety management systems rely on data and analytics to identify patterns and trends related to safety incidents. By examining historical incident data, organizations can pinpoint recurring issues and focus their resources on addressing these areas. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are allocated where they are needed most, making safety efforts more efficient and effective.
d. Continuous Improvement: SMS promotes a culture of continuous improvement. By analyzing past incidents and near misses, organizations can learn from their mistakes and develop strategies to prevent similar incidents in the future. This feedback loop ensures that safety measures are continually refined and enhanced.
e. Employee Involvement: SMS often encourages employees to actively participate in hazard identification and incident prevention. Workers on the front lines are often best positioned to spot potential risks. Engaging employees in the safety process not only helps prevent incidents but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for safety within the workforce.
f. Proactive vs. Reactive: Traditional safety approaches tend to be reactive, addressing safety issues after incidents occur. SMS shifts the focus to a proactive stance, where the goal is to prevent incidents from happening in the first place. This proactive approach is more cost-effective, as it avoids the expenses associated with investigations, medical bills, and potential legal issues that follow workplace incidents.
In summary, the improved incident prevention aspect of Safety Management Systems is all about anticipating and addressing safety hazards before they lead to workplace accidents. It promotes a culture of safety, data-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement to create a secure work environment for employees while saving organizations time and resources that would otherwise be spent reacting to incidents. This proactive approach is a key component of modern workplace safety and is vital for any organization aiming to protect its employees and maintain its reputation.
Streamlined Compliance:
Ensuring compliance with safety regulations and industry standards is a critical aspect of safety management. Safety Management Systems (SMS) streamline compliance in various ways:
a. Automated Compliance Tracking: SMS integrates compliance tracking mechanisms that automatically monitor and manage safety-related regulations, standards, and requirements. This automation reduces the administrative burden of compliance tracking, ensuring that organizations stay up-to-date and aligned with the latest safety mandates.
b. Customized Checklists: SMS often allows organizations to create customized safety checklists tailored to their specific industry, location, or operation. These checklists ensure that all relevant compliance measures are addressed, reducing the risk of overlooked requirements.
c. Documentation Management: Compliance often involves extensive documentation, such as safety manuals, incident reports, and training records. SMS provides a centralized platform for managing and organizing this documentation, making it readily accessible for audits or inspections.
d. Real-Time Updates: Safety regulations and industry standards are subject to change. SMS software can provide real-time updates on regulatory changes, ensuring that organizations promptly adapt to new requirements to maintain compliance.
e. Audit Trails: SMS generates detailed audit trails that track every action and change within the system. These audit trails provide a transparent record of compliance-related activities, which can be invaluable during audits or regulatory inquiries.
f. Accountability: Safety management systems establish clear lines of accountability within an organization. They assign responsibilities for compliance tasks to specific individuals or departments, ensuring that no critical compliance tasks fall through the cracks.
g. Reporting and Documentation: SMS assists in the generation of compliance reports. These reports are not only vital for demonstrating adherence to regulations but also for identifying areas where improvement is needed to meet compliance standards.
h. Cost Savings: Failing to comply with safety regulations can lead to costly fines, legal liabilities, and damage to an organization’s reputation. SMS reduces the risk of non-compliance, potentially saving an organization substantial financial and reputational losses.
In summary, streamlined compliance through Safety Management Systems helps organizations navigate the complex landscape of safety regulations and standards with efficiency and accuracy. It minimizes the risk of non-compliance, reduces administrative overhead, and ensures that safety practices remain in accordance with the ever-evolving requirements of the industry. Compliance isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about creating a safer work environment and maintaining trust with employees, clients, and regulatory bodies.

-
Efficient Training and Learning:
Incorporating Learning Management Systems (LMS) and Training Management Systems (TMS) into Safety Management Systems (SMS) significantly enhances the training and learning aspects of workplace safety. Here’s a closer look at how these systems work together to improve safety training:
a. Accessibility and Convenience: LMS and TMS integrated into SMS make safety training materials accessible to employees at their convenience. This accessibility is particularly valuable for remote or dispersed workforces, enabling employees to access training modules online from anywhere, anytime.
b. Standardized Training: SMS ensures that safety training is standardized across the organization. This means that all employees receive consistent, up-to-date training materials, reducing the risk of knowledge gaps or misunderstandings regarding safety procedures.
c. Compliance Training: SMS with integrated LMS/TMS tracks and manages compliance training requirements. This is especially important for industries with strict regulatory training mandates, as it ensures that every employee receives the necessary training to remain compliant with safety regulations.
d. Self-Paced Learning: The integration of LMS/TMS into SMS allows for self-paced learning. Employees can progress through safety training modules at their own speed, ensuring they grasp the content thoroughly before moving on. This is particularly beneficial for employees with varying learning paces and styles.
e. Progress Tracking: SMS with LMS/TMS offers the ability to track and report on employee training progress. Supervisors and safety managers can easily monitor who has completed training and who may require additional support, ensuring that everyone is up to date on safety protocols.
f. Flexibility: SMS allows organizations to create a flexible and adaptable training schedule. This can be especially useful for organizations with shift work or varying work hours, ensuring that every employee can access training without disrupting their work responsibilities.
g. Scalability: For growing organizations, SMS with LMS/TMS can seamlessly scale to accommodate an increasing workforce. New employees can quickly access training materials and get up to speed on safety procedures.
h. Continuous Learning Culture: By integrating learning into the SMS, organizations can foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Employees are encouraged to regularly engage with safety materials, keeping their knowledge and skills up to date.
i. Reduced Training Costs: SMS integrated with LMS/TMS can lead to reduced training costs. Traditional classroom-style training often incurs expenses related to travel, printed materials, and instructor fees. Online training materials are cost-effective, saving both time and money.
In summary, efficient training and learning through the integration of LMS and TMS into Safety Management Systems ensure that employees receive standardized, accessible, and up-to-date safety training. This not only enhances workplace safety but also creates a culture of continuous learning, where employees are empowered to take responsibility for their own safety education. The ability to track progress and compliance ensures that organizations maintain high safety standards and adapt to changing training requirements efficiently.
-
Enhanced Data Management:
Effective data management is a cornerstone of Safety Management Systems (SMS). Here’s a more detailed explanation of how SMS enhances data management for improved safety:
a. Data Collection and Storage: SMS provides a centralized platform for collecting and storing safety-related data. This includes incident reports, safety audits, hazard assessments, and training records. Storing this information in one location ensures that it’s easily accessible and well-organized.
b. Data Analysis: SMS offers robust data analysis tools. By examining this data, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and areas that require attention. For example, if incident data shows a recurring type of accident, the organization can take specific measures to address the root cause.
c. Predictive Analytics: Some advanced SMS incorporate predictive analytics. These tools use historical data to predict potential safety issues and identify areas where preventive action is needed. This proactive approach helps organizations address risks before they escalate into incidents.
d. Performance Metrics: SMS allows organizations to define and track key safety performance metrics. This includes indicators like incident rates, near-miss reporting, and the effectiveness of safety training programs. These metrics help assess safety program performance and guide decision-making.
e. Custom Reporting: SMS software often includes customizable reporting features. This means that organizations can generate reports tailored to their specific needs and requirements. Custom reports can be invaluable for presenting data to management, regulatory bodies, or for internal reviews.
f. Compliance Tracking: As mentioned in benefit #2, SMS assists in tracking compliance data, including the status of safety-related training and regulatory adherence. This ensures that the organization can readily demonstrate its compliance during audits or inspections.
g. Data Security: Data security is a paramount concern in SMS. These systems typically include robust security measures to protect sensitive safety-related information. This safeguards both employee data and organizational information from potential breaches.
h. Historical Records: SMS maintains historical records of safety-related data. This historical perspective is invaluable for understanding how safety performance has evolved over time and for identifying areas where improvements have been made.
i. Informed Decision-Making: By leveraging the data collected and analyzed through SMS, organizations can make informed decisions. For instance, they can allocate resources to areas where data indicates higher safety risks or enhance safety training programs where performance metrics suggest a need for improvement.
In summary, Safety Management Systems are data-centric tools that empower organizations to collect, analyze, and act upon safety-related data. This data-driven approach is essential for understanding safety performance, identifying trends and areas for improvement, and making informed decisions to enhance workplace safety. Effective data management through SMS is not just about record-keeping; it’s about using data as a powerful tool to proactively prevent incidents and continuously improve safety practices.
-
Real-Time Reporting:
One of the significant advantages of Safety Management Systems (SMS) is their ability to facilitate real-time reporting of safety-related incidents and observations. Here’s a closer look at how real-time reporting benefits workplace safety:
a. Immediate Incident Reporting: SMS allows employees to report safety incidents, near-misses, and hazards as they occur. This real-time reporting enables organizations to respond promptly to mitigate potential risks and prevent incidents from worsening. Immediate reporting is crucial for addressing safety issues before they escalate. For a closer look at an incident reporting module review our incident management software that is part of our safety management system.
b. Faster Corrective Actions: With real-time reporting, corrective actions can be initiated swiftly. Safety managers and supervisors can access incident reports immediately, allowing them to take necessary steps to resolve issues and prevent similar incidents in the future. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and potential injuries.
c. Enhanced Visibility: Real-time reporting provides real-time visibility into safety issues. It allows safety managers to monitor the frequency and nature of incidents, which is essential for identifying trends, patterns, and recurring problems. This visibility enables data-driven decision-making to improve safety practices.
d. Improved Accountability: Real-time reporting enhances accountability. When employees are encouraged to report incidents promptly, it fosters a sense of responsibility for safety within the organization. This accountability extends to all levels of the workforce, from frontline workers to management.
e. Timely Documentation: Real-time reporting ensures that all safety-related incidents and observations are accurately documented. This documentation is crucial for maintaining an accurate historical record of safety events, which can be valuable for audits, regulatory compliance, and legal purposes.
f. Communication and Collaboration: SMS with real-time reporting capabilities fosters improved communication and collaboration among team members. Employees can share safety concerns, insights, and observations quickly, promoting a culture of openness and information exchange.
g. Proactive Preventive Measures: Real-time reporting not only addresses incidents but also identifies potential hazards. When employees report hazards in real-time, safety managers can take preventive measures to eliminate or mitigate these risks before they lead to accidents.
h. Employee Engagement: Encouraging employees to report incidents and hazards in real-time engages them in the safety process. They feel that their input is valued, which, in turn, can lead to a more proactive and safety-conscious workforce.
i. Continuous Improvement: Real-time reporting contributes to a culture of continuous improvement. By addressing incidents and hazards as they happen, organizations learn from these experiences and continually enhance their safety practices.
In summary, real-time reporting through Safety Management Systems is a critical tool for maintaining a proactive approach to workplace safety. It empowers employees to report incidents and hazards promptly, leading to faster corrective actions, enhanced visibility into safety issues, and a greater sense of accountability within the organization. Real-time reporting is a cornerstone of a culture of safety that emphasizes incident prevention and continuous improvement.
-
Cultivating a Safety Culture:
Cultivating a safety culture is one of the most significant benefits of implementing Safety Management Systems (SMS). This aspect goes beyond compliance and processes; it focuses on shaping the collective mindset of employees and management towards prioritizing safety. Here’s an in-depth exploration of how SMS contributes to fostering a strong safety culture:
a. Employee Involvement: SMS encourages active employee involvement in safety initiatives. It empowers workers to participate in incident reporting, hazard identification, and safety training. This involvement not only makes employees feel invested in their safety but also reinforces the idea that safety is everyone’s responsibility.
b. Communication and Transparency: SMS promotes open and transparent communication regarding safety matters. It enables employees to discuss safety concerns, share insights, and report incidents without fear of reprisals. This open dialogue ensures that potential safety issues are addressed promptly.
c. Learning from Incidents: SMS encourages organizations to view incidents as learning opportunities rather than assigning blame. By analyzing incidents and near-misses, organizations can identify root causes, implement corrective actions, and prevent similar incidents. This approach fosters a culture of continuous learning from experiences.
d. Safety Leadership: A safety culture starts at the top. SMS emphasizes the importance of safety leadership, where executives, managers, and supervisors set a strong example by consistently following safety procedures. When leadership actively prioritizes safety, it influences the entire organization.
e. Empowerment: SMS empowers employees to take control of their safety. When they have access to safety training, reporting mechanisms, and the knowledge that their concerns are valued, they become proactive participants in their own safety and the safety of their colleagues.
f. Recognition and Rewards: Safety management systems often incorporate recognition and reward programs for employees who actively contribute to safety. These programs motivate employees to actively engage in safety initiatives and reinforce the idea that safety is a collective effort.
g. Hazard Prevention: By focusing on hazard identification and proactive safety measures, SMS underscores the importance of preventing incidents before they occur. A safety culture revolves around avoiding accidents, rather than reacting to them.
h. Adaptability and Continuous Improvement: SMS encourages organizations to adapt and improve safety practices continually. This adaptability ensures that safety remains relevant in an ever-changing work environment, and that processes and procedures evolve to address emerging risks.
i. Employee Well-Being: Beyond physical safety, SMS also promotes employee well-being. This includes addressing mental health concerns, work-life balance, and overall job satisfaction, recognizing that a holistic approach to well-being contributes to a comprehensive safety culture.
In summary, cultivating a safety culture through Safety Management Systems is about creating a workplace environment where safety is a shared value and a collective responsibility. It involves proactive involvement, open communication, a commitment to learning from incidents, and a top-down demonstration of leadership. A strong safety culture not only leads to a safer workplace but also enhances employee morale, job satisfaction, and the overall success of the organization.
In the coming sections of this article, we will delve deeper into each of these benefits to provide a comprehensive understanding of how Safety Management Systems and associated tools can significantly enhance workplace safety. Whether you’re a small business or a large corporation, these systems can make a substantial difference in keeping your workforce safe and your operations compliant. Stay tuned to learn more about how to harness the power of SMS, LMS, TMS, and safety software for a safer, more productive workplace.
Additional Articles

National Parks to Petrochemicals: How Sarah Anderson Became a Champion for Safer Workplaces
From national parks to oil refineries, Sarah Anderson’s journey into safety leadership proves that trust, presence, and purpose can reshape how workplaces protect people. … Read More

Top 10 Red Flags in Safety Audits and How to Avoid Them
Regardless of your industry in the UK, training is a crucial aspect of ensuring the smooth operation of your business.
… Read More